Introduction
AGC stands for Auto Gain Control, which is a technique used in electronic systems to automatically adjust the gain of an amplifier or similar component to maintain a relatively constant output level. This is important because input signals to electronic systems can vary widely in strength, and without AGC, the output level would also vary widely, leading to poor system performance.
Examples of electronic devices that use AGC include audio amplifiers, which use AGC to maintain a constant volume level despite variations in the input signal strength; video cameras, which use AGC to adjust the brightness of the image depending on lighting conditions; and radios, which use AGC to compensate for changes in signal strength due to distance from the transmitter or interference. Other devices that may use AGC include radar systems, data communication systems, and medical imaging equipment.
How does AGC work?
AGC (Auto Gain Control) works by automatically adjusting the gain of an electronic system to maintain a relatively constant output level. The basic principle behind AGC is to detect the output level of the system and use this information to adjust the gain of the amplifier or other components in the system.
The specific method used to implement AGC can vary depending on the application, but typically involves the following steps:
Detection: The output level of the system is detected using a sensor or detector circuit. This may involve measuring the peak amplitude, RMS value, or logarithmic ratio of the output signal.
Comparison: The detected output level is compared to a reference level. This reference level may be fixed or may vary depending on the specific application.
Control: Based on the comparison between the detected output level and the reference level, a control signal is generated that is used to adjust the gain of the amplifier or other components in the system. This control signal may be analog or digital, and may be used to adjust the gain of a variable gain amplifier or to control the bias current of a transistor amplifier.
The specific type of AGC circuit used can vary depending on the application. For example, peak detecting AGC circuits are commonly used in audio amplifiers to maintain a constant volume level, while RMS AGC circuits are commonly used in radio receivers to maintain a constant audio output level.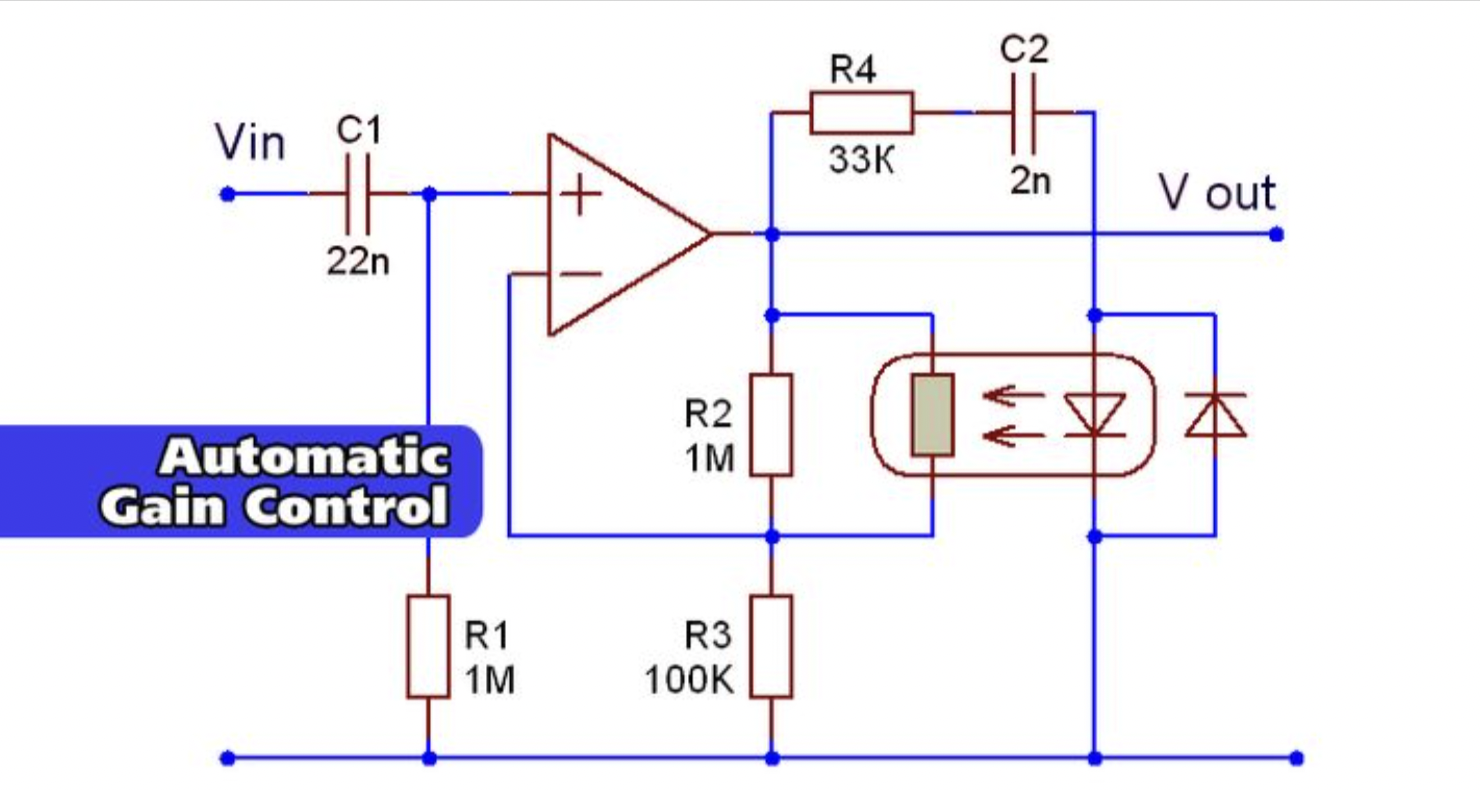
Advantages of AGC
AGC (Auto Gain Control) can provide several benefits in electronic systems, including improved signal-to-noise ratio, increased dynamic range, and reduced distortion. AGC helps to maintain a constant output level despite variations in the input signal strength, which improves the signal-to-noise ratio of the system, allows it to handle a wider range of input signal strengths, and prevents the amplifier or other components from being overdriven, reducing the likelihood of distortion. Additionally, AGC can compensate for changes in input signal strength, such as in the case of a radio receiver moving out of range of a transmitter, by automatically adjusting the gain of the system to maintain a relatively constant output level, making it easier to hear the signal. Overall, AGC is an important technique in electronic systems that can help to ensure optimal system performance under a wide range of operating conditions.
Limitations of AGC
While AGC (Auto Gain Control) can provide several benefits in electronic systems, there are also some limitations to its use. One potential limitation is the potential for signal clipping and distortion if the AGC circuit is not properly designed. If the AGC circuit is too aggressive in adjusting the gain of the amplifier, it may cause the signal to clip or distort, which can degrade the quality of the output signal. This can be particularly problematic in audio systems, where distortion can result in unpleasant or even damaging sounds.
Another potential limitation of AGC is that it can sometimes be detrimental to the performance of certain electronic systems, such as audio amplifiers that are designed for specific input levels. In these cases, the use of AGC may actually reduce the performance of the amplifier, as it may cause the amplifier to operate outside of its optimal range. For example, if an audio amplifier is designed to operate at a specific input level, the use of AGC may cause the amplifier to operate outside of this range, leading to reduced performance and increased distortion.
Overall, while AGC can be a useful technique for maintaining a relatively constant output level in electronic systems, it is important to understand its limitations and to design AGC circuits carefully to avoid potential problems such as signal clipping, distortion, and reduced performance. In some cases, alternative techniques such as manual gain control (MGC) may be more appropriate for achieving optimal performance in electronic systems.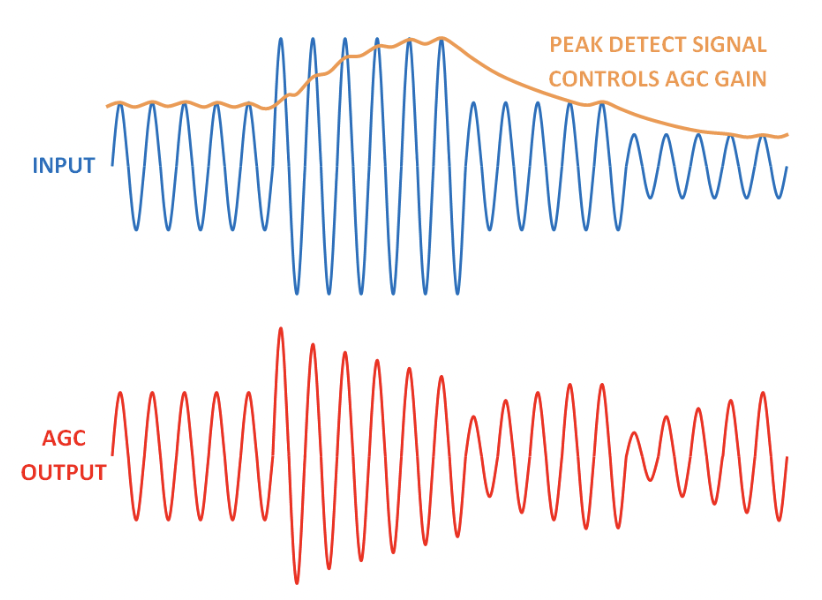
Applications of AGC
AGC (Auto Gain Control) is widely used in various electronic systems. It is commonly used in audio amplifiers to maintain a constant volume level and in video cameras to adjust brightness. AGC is also used in radio receivers to maintain constant audio output level despite variations in signal strength. AGC helps to improve system performance by reducing distortion, improving signal-to-noise ratio, and increasing dynamic range. However, it must be carefully designed to avoid potential problems such as signal clipping and distortion.
The Nearity A20s microphone is an excellent example of how AGC (Auto Gain Control) can be used in audio equipment to address the specific challenges of conference room communication. With its 8-element array and beamforming technology, the A20s can eliminate acoustic and room echo, ensuring that all participants in the meeting can be heard equally. This can help to address challenges such as variations in the recording level of different audio sources and differences in the loudness of different speakers.
Conclusion
AGC (Auto Gain Control) is a widely used technique in electronic systems that automatically adjusts the gain of an amplifier or similar component to maintain a relatively constant output level. AGC is used in various electronic devices, such as audio equipment, video cameras, and radios, to address specific challenges and improve system performance. AGC can provide several benefits, including improved signal-to-noise ratio, increased dynamic range, and reduced distortion. However, AGC must be carefully designed to avoid potential problems such as signal clipping and distortion. Understanding how AGC works and its limitations is crucial for achieving optimal performance in electronic systems.



