TL; DR
Bluetooth has become a ubiquitous short-range wireless standard, enabling seamless communication among different devices. This blog first explains the technology of Bluetooth, then categorizes its core profiles. The evolution of Bluetooth from its 1 Mbps beginnings to the feature-rich 5.3 version is traced, emphasizing enhancements in different parameters. Key applications in hands-free calling, asset tracking, smart homes, and health monitoring are illustrated. A detailed firmware-upgrade procedure ensures users can leverage new features, while FAQs demystify Bluetooth’s Viking-inspired name, original developers, and timeline. The article equips technical and business audiences to optimize Bluetooth deployment and stay current with evolving standards.
Let’s be honest—Bluetooth has become one of those things we use every single day without even thinking about it. Whether you're blasting your favorite playlist on a speakerphone during a backyard BBQ, hopping on a Zoom call with a Bluetooth conference camera, or using wireless earbuds while working out—Bluetooth is there, quietly making life easier. In this post, we will break it all down—from the basics to the cutting edge—and see how Bluetooth is evolving, where it’s used, and why staying current with the newest bluetooth generation actually matters (especially if you care about call quality, battery life, and connection reliability).
Overview of Bluetooth: Definition,Basic Technology, Types & Features
Bluetooth isn’t just another buzzword—it’s the foundation of seamless wireless connectivity. From sharing photos with friends to powering our favorite conference cameras, Bluetooth’s evolution has been all about making our lives simpler and more connected.
What is Bluetooth?
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless communication protocol that lets devices “talk” to each other over radios instead of cables. Imagine your smartphone sending audio to a speakerphone during a call without a single wire—Bluetooth makes that happen. It was designed to simplify device pairing and reduce the proliferation of ports and cables on gadgets.

How does Bluetooth work?
At its core, Bluetooth operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM band (the same range that your Wi-Fi and microwave oven use). Here’s a simplified step-by-step of the process:
- Discovery & Inquiry: Your device sends out an “Are you there?” signal.
- Paging & Connection: The responding device says “Yes, I’m here,” and they negotiate security keys.
- Pairing & Bonding: With a shared PIN or secure key exchange, the devices establish trust.
✎When Bluetooth devices connect with one another, a small network called a piconet is formed.
▶There can be up to eight devices in one piconet at any one time.
▶Even though there is a connection between devices, that connection is not always open to communication. One of the devices in the piconet will take the role of the master and the rest will be slaves.
- Data Exchange: Audio, files, or control commands flow back and forth—encrypted and managed by profiles like Advanced Audio Distribution Profile (A2DP) for audio or HID for keyboards.
Under the hood, Bluetooth uses frequency-hopping spread spectrum (FHSS), rapidly switching frequencies to minimize interference and maximize stability. In other words, this will allow the devices to continue to communicate without each device hopping over to different frequencies and losing the connection.
What is the Type of Bluetooth?
Bluetooth comes in a few core categories, each tailored to specific use cases:
- Classic Bluetooth (BR/EDR): Best for high-throughput audio (think stereo speakerphones).
- Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE): Optimized for minimal power draw—ideal for fitness trackers and IoT sensors.
- Bluetooth Mesh: Enables many-to-many device networks, perfect for smart lighting or building automation.
Depending on what you need—rich audio for your conference camera or battery-sipping connectivity for a wireless microphone—you’ll choose the type that fits.
The Pros and Cons of Bluetooth
Pros of Bluetooth
- Ubiquity: Found on nearly every smartphone, laptop, and tablet.
- Simplicity: Pairing is usually a two-tap affair.
- Low Power: Especially with BLE for always-on sensors.
Cons of Bluetooth
- Range Limitations: Typically up to 100 meters for Class 1 devices, but often less in real-world settings.
- Bandwidth Constraints: Not ideal for ultra-high-definition audio or large file transfers.
- Interference: Crowded 2.4 GHz band can lead to dropouts if not managed properly.
Evolution of Different Bluetooth Versions: newest bluetooth technology
Bluetooth’s journey from version 1.0 to the newest Bluetooth technology is a story of constant refinement—boosting speed, extending range, and slashing power demands. Here’s a quick timeline:
- Bluetooth 1.0 & 1.1 (1999–2001): The groundwork—basic voice and data, up to 1 Mbps.
- Bluetooth 2.0 + EDR (2004): Introduced Enhanced Data Rate for up to 3 Mbps.
- Bluetooth 3.0 + HS (2009): High Speed mode using Wi-Fi for bursts up to 24 Mbps.
- Bluetooth 4.0 (2010): Debut of BLE (Bluetooth Smart), a game-changer for wearables.
- Bluetooth 4.2 (2014): Improved privacy, throughput, and IoT support.
- Bluetooth 5.0 (2016): Double BLE range and speed, ideal for larger venues.
- Bluetooth 5.1 (2019): Added direction-finding for indoor positioning.
- Bluetooth 5.2 (2020): LE Audio with AAC/LC3 codec support, multi-stream audio.
- Bluetooth 5.3 (2021): Efficiency tweaks like ISO channel improvements for more stable audio.
Each iteration has expanded what we can do—from streaming crystal-clear voice on a speakerphone to deploying battery-powered BLE beacons for asset tracking in warehouses.
Difference between Bluetooth 5.0 and 5.3: difference between Bluetooth 5.0 and 5.3
To help you compare Bluetooth 5.0 with Bluetooth 5.3, here’s an Excel-style breakdown you can drop directly into your spreadsheet:
td {white-space:nowrap;border:0.5pt solid #dee0e3;font-size:10pt;font-style:normal;font-weight:normal;vertical-align:middle;word-break:normal;word-wrap:normal;}
Feature | Bluetooth 5.0 | Bluetooth 5.3 |
Release Year | 2016 | 2021 |
BLE Range | Up to 240 m (in open space) | Similar, with minor radio optimizations |
BLE Speed | Up to 2 Mbps | Same LE Data Rate, but improved packet efficiency |
Audio Support | Basic audio over Classic Bluetooth | LE Audio with LC3 codec—better quality at lower bitrates |
Direction Finding | Not supported | Supported via AoA/AoD for indoor positioning |
ISO (Isochronous) Channels | Not supported | Supported—enables synchronized streams for multi-device audio |
Periodic Advertising with Sync Transfer | Limited functionality | Enhanced—improves beacon and mesh network performance |
Energy Efficiency | Good, but no channel classification | Adds Channel Classification—optimizes scanning and reduces power |
Widespread Applications of Bluetooth Technology
Bluetooth’s versatility makes it the backbone of countless modern conveniences:
- Audio Streaming: From wireless headphones and speakerphones to multi-room audio systems, Bluetooth is the go-to for cable-free sound.
- Hands-Free Calling: In cars or conference rooms, Bluetooth lets you talk without holding a mic—perfect for our professional-grade conference cameras with built-in mics.
- Data Transfer: Share photos, contacts, or large files directly device-to-device.
- IoT & Smart Homes: BLE sensors control lights, doors, and thermostats—mesh networking scales from one room to entire buildings.
- Health & Fitness: Heart rate monitors, smart scales, and wearables use BLE to keep tabs on your stats in real time.
- Location & Tracking: Find lost keys or guide robots in warehouses using direction-finding and beacon tech from Bluetooth 5.0 onward.
Whether you’re outfitting a huddle room with our conference camera and speakerphone bundle or tracking inventory with BLE tags, Bluetooth’s flexibility keeps you connected.
Step by Step Guide on Upgrading the Latest Bluetooth version: latest bluetooth version
Upgrading your devices (latest Bluetooth version) can feel daunting, but I’ll break it down:
- Check Compatibility
- Visit your device’s settings > “About” > “Bluetooth Version” (or consult the manual).
- Ensure firmware updates from your manufacturer support the newest Bluetooth.
- Update Device Firmware
- Windows: Run “Windows Update” or download drivers from the PC maker.
- macOS: Use “Software Update” in System Preferences.
- Mobile (iOS/Android): Install the latest OS version via Settings > General > Software Update.
- Update Peripheral Devices
- Speakerphones, microphones, and cameras often have companion apps—open the app, go to “Device Info,” and click “Check for Firmware Update.”
- Follow on-screen instructions; don’t power down mid-update!
- Re-Pair Devices
- Once firmware is current, forget the old Bluetooth pairing in your settings.
- Rediscover and re-pair to ensure you’re using the new features (like LE Audio or direction finding).
- Test New Features
- Try multi-stream audio on our latest speakerphones.
- Use indoor positioning if you have a conference space with Bluetooth 5.1 beacons.
- Measure battery life improvements on BLE devices.
- Troubleshoot Common Issues
- Interference: Move devices away from other 2.4 GHz sources.
- Stability: Ensure drivers/firmware match OS updates.
- Connection Drops: Check power-saving settings—sometimes aggressive sleep modes can disrupt pairing.
By following these steps, you’ll be harnessing the newest Bluetooth technology in no time, whether it’s in a home office setup or a fully-equipped boardroom.
FAQs
Why is it called Bluetooth?
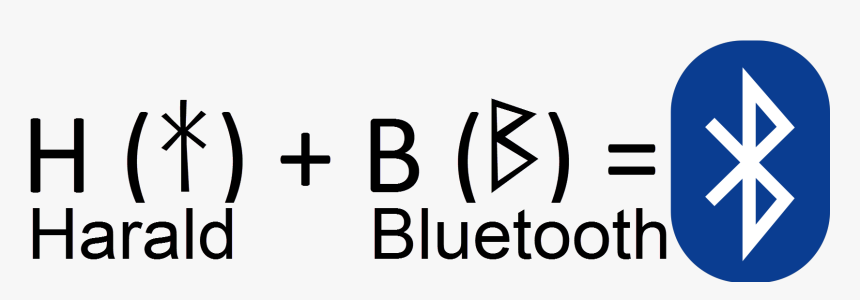
Believe it or not, Bluetooth was named after Harald “Bluetooth” Gormsson, a 10th-century Viking king of Denmark from 940 to 985 AD who united warring tribes—much like the technology unites devices. The following picture is the origin of the logo.
Who developed Bluetooth?
The technology sprang from Ericsson, a Swedish telecom giant. Today, the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG)—a consortium of thousands of companies—oversees its evolution and ensures interoperability.
When did Bluetooth first become available?
Bluetooth 1.0 launched in 1999, but it wasn’t until 2004’s Bluetooth 2.0 + EDR that the protocol gained real-world traction thanks to faster data rates.
Final Thought
Bluetooth has come a long way from its humble 1 Mbps beginnings to today’s multi-stream, mesh-enabled marvels. Whether you’re a remote worker, a tech hobbyist, or an IT manager rolling out conference cameras and speakerphones across multiple rooms, understanding the latest Bluetooth version, the difference between Bluetooth 5.0 and 5.3, and the advantages of BLE will help you make smarter decisions—and keep your meetings, music, and IoT devices humming smoothly.
🚀Ready to experience crystal-clear audio on your next video call? 🎯 With the Nearity A22 Bluetooth Conference Speakerphone, you’re upgrading your entire meeting experience. Whether you're in a small huddle room or a large boardroom, the A22 adapts with powerful AI noise cancellation, full-room voice pickup, and seamless connectivity.
👉 Upgrade to smarter meetings with Nearity. Don’t let outdated tech hold you back 🌈










